In May 2023, the Cabinet Secretary for the National Treasury presented the Finance Bill 2023 to the National Assembly for discussion and potential enactment into the Finance Act 2023. The bill includes several proposals, one of which is the introduction of a 3.0% levy on employees’ gross monthly income. This along with a corresponding contribution from employers. This initiative aims to provide funding for Kenya’s affordable housing project. The funds will be directed towards the National Housing Development Fund (NHDF). The NHDF was initially established in 2018 under the Finance Act and is overseen by the National Housing Corporation (NHC). NHFD’s primary objective is to raise funds from various sources to provide affordable housing solutions to the people of Kenya.
Table of Contents
What is Affordable Housing?
The Economic Times defines affordable housing as housing units that have reasonable prices and within the financial means of low- and moderate-income individuals and families. It is typically characterized by housing options that require a lower percentage of a household’s income compared to the prevailing market rates.
Based on the government’s BluePrint, affordable housing units typically range from Kshs. 1 million to Kshs. 3 million per unit on average. This price range allows for affordability within the budget of two individuals earning a minimum of Kshs. 50,000 each per month, which represents the median income in Kenya.
Kenya Housing Deficit
Kenya’s current housing deficit stands at 200,000 units annually. To address this deficit, the government launched the Affordable Housing Program in December 2017. The program’s objective was to construct and deliver 500,000 housing units by December 2022. The prices ranging from Kshs 1 million to Kshs 3 million for one to three-bedroom units, respectively.
The housing initiative has however faced several challenges in realizing its full potential. These difficulties primarily stem from financial constraints caused by inadequate budget allocation, resulting in project delays. For example, in the FY ‘2022/23 Budget, the Affordable Housing Program was allocated Kshs 27.7 billion, while a minimum of Kshs 416 billion is required to meet the government’s target of constructing 250,000 homes annually. Using this calculation, the budgetary provisions only cover 6.65 percent of the overall goal.
In order to generate funds, the government is exploring multiple avenues, including the proposed NHDF tax.
How will the Housing Fund work?
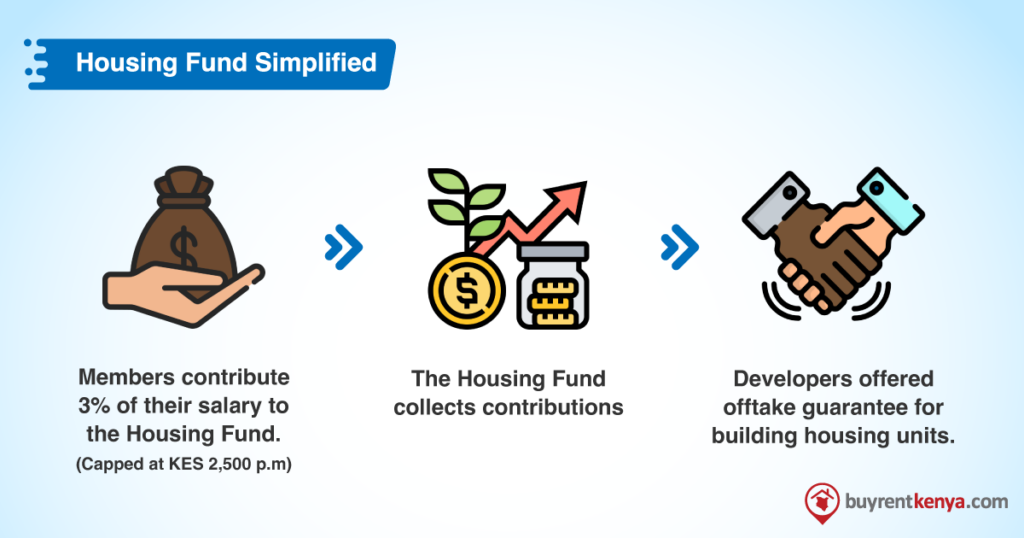
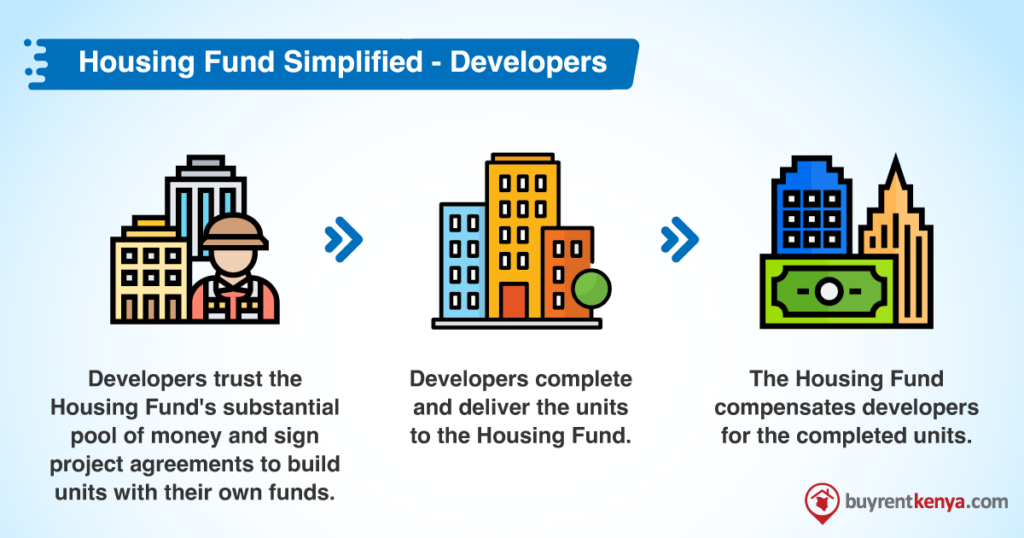
Developers in the affordable housing sector face several limitations and challenges. Without guarantees on who will buy their units, developers often opt for cherry-picking locations for their projects instead of building a large number of units. The risk perception associated with potential buyers often leads to higher pricing and the need for more upfront equity, which is more expensive than debt financing. Additionally, developers face long delivery periods as they need to align sales with funding drawdowns.
Buyers, on the other hand, struggle with inadequate funding options and lack of eligibility for mortgages due to irregular cash flows. Existing mortgages are often unaffordable due to high interest rates and short repayment periods. Moreover, there is a limited supply of affordable housing units in areas connected to transportation corridors and economic centers, further exacerbating the challenges in accessing affordable housing.
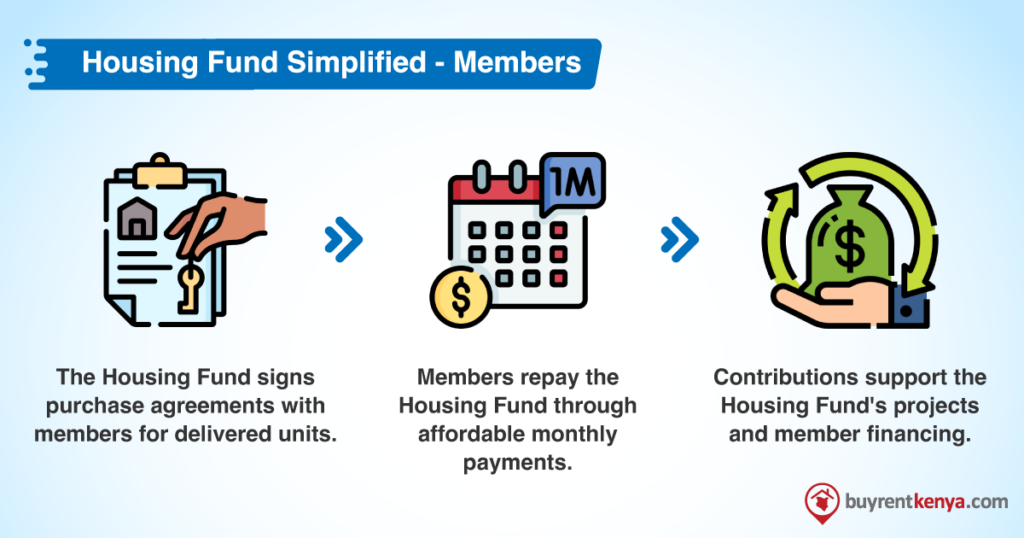
The housing fund will therefore act as an intermediary between developers and buyers. It aims to raise capital, provide developers with sales certainty through an off-take commitment, and offer accessible financing options to home buyers via a National Tenant Purchase Scheme.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the introduction of the National Housing Development Fund (NHDF) and the proposed 3% housing levy in Kenya’s Finance Bill 2023 signify the government’s commitment to addressing the country’s housing deficit and making affordable housing accessible to its citizens. The NHDF aims to raise funds, provide sales certainty to developers, and offer accessible financing options to home buyers.
However, the affordable housing initiative faces challenges such as financial constraints, limited supply, and affordability issues for developers and buyers. Nonetheless, with the implementation of the NHDF and the housing levy, the government hopes to realize the affordable housing initiative. It remains crucial for stakeholders to collaborate and address these challenge. This will ensure the success of Kenya’s affordable housing program and meet the housing needs of the population.



